Continual Improvement and Nonconformity and corrective action – Lecture 24
Lecture summary:
- You must determine and select improvements and then put the action in place to meet customer’s requirements and enhance any customer satisfaction
- You have to react when nonconformity occurs, including nonconformities that were reported during a complaint
- You are required to continually improve your products and services to meet customer requirements and to measure the effectiveness of your processes
In this part of ISO 9001 - Improvement means, in a way, finding the parameters that affect the realization of goals and submitting them to change. The challenge is to identify the specific processes that have the most effect on the conformity of goods to customer satisfaction.
The ISO 9001 Standard requires the identification of those poor in performance and effectiveness processes or process outputs (products or services) and the implementation of controlled changes that will improve them.
Improving the performance of the QMS
The performance of the QMS is monitored, measured, and evaluated through many quality tools and methods suggested in the standard. An analysis of process performance may result in improvement, redesign, or reengineering of the QMS activities.
The ISO 9001 Standard expects you to define which inputs and sources of information in the QMS may indicate the need for improvement. And then, you are required to implement any necessary actions to achieve the improvement that you identified. And each action refers to its relevant ISO 9001 Standard requirement, for example:
- Changes in the QMS
- Changes in the planning of processes
- Changes to requirements for products and services
- Design and development changes
- Control of changes for production or service provision
Nonconformity and Corrective Actions
Corrective action is one of the basic factors of quality management and is crucial for the sustainable improvement of your QMS. The fundamental idea of corrective action is promoting a systematic analysis of quality problems that have already occurred, and the elimination of any root causes of nonconformities through implementing controlled measures.
Be aware, corrective actions may trigger changes or updates to your QMS. Changes may occur in quality policy, quality objectives, processes, procedures, work instructions, resources, infrastructures, process environment, and documented information. This is why you have to evaluate where such changes may occur when initiating corrective action.
Continual Improvement
Continual improvement is a type of learning where the organization evaluates itself constantly, makes informed judgments and decisions based on the
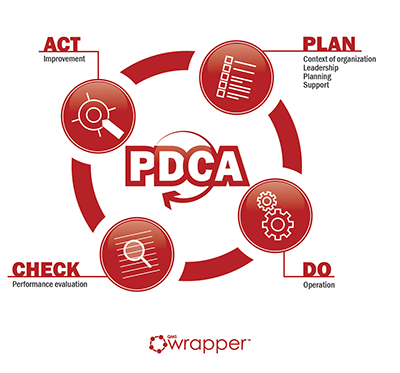
results of such analyses, and initiates actions for improvement. The ISO 9001 standard promotes this approach popular called the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle.
The principle of the PDCA cycle exists in all of our daily business activities. We use it both formally and informally, and the PDCA cycle never ends. Its objective is to maintain continuous improvement. The method combines planning, implementing, controlling, and improving the different operations of the QMS.
ISO 9001 implementation: Mandatory documents and records
Management review – Lecture 23
Internal audit – Lecture 22