Checklist for implementing a QMS for ISO 9001-2015
What is ISO 9001?
ISO 9001 is a process standard for a quality management system, known worldwide.
This standard is suitable for any size company or organizations
that wants to meet their costumer’s and regulatory requirements and consistently improve.
PHASE 1: PLANNING AND DESIGN
Step 1
Top management commitment
The top management should show a commitment and
a determination to implement ISO 9001
or one of the associated standards (for example ISO 13485)
the quality management system in the organization.
They must be convinced that registration and certification
will enable the organization to show their commitment to quality to their customers.
Step 2
Establish a
Representative
Management Representative should be a person
who coordinates and oversees the progress of implementation.
He or she must be certified in ISO 9001 and
become a key person between the top management and ISO register
Responsibilities of a management representative

Step 3
Start ISO 9001 awareness training
The training should be structured for different categories
of employees (managers, supervisors…) and should cover:
- the basic concepts of quality systems and standard
- the overall impact on the company’s strategic goals
- the changed work processes, and likely work culture
implications of the quality
As an additional training about writing quality manuals,
procedures and work instructions would be also necessary.
Step 4
Perform a Gap Analysis
In this step, you should compare your existing quality system
with the requirements of the ISO 9001 standard.
It has a goal of determining what processes and procedures
your company already meet ISO 9001 requirements,
what needs to be modified and what needs
to be created to meet ISO 9001 requirements.
Steps of gap assessment
- 1. Determinate
Determining the present operations and processes which already exists
- 2. Analyze
Analyzing the relevant sections of the ISO 9001 standard to determine what is actually required
- 3. Document
Documenting the “gaps”
This can be performed internally or by externally by an experienced ISO 9000 consulting firm.
Step 5
Create a documented implementation plan
Elements of implementation plan should be thorough and specific, detailing:
- quality documentation to be developed
- relevant ISO 9001 standard section
- person/team responsible
- required approvals
- required training
- required resources
- estimated completion date
A Gantt chart should be made, reviewed and approved by the top management.
After approval, the Management Representative should control,
review and update the plan as documentation and the implementation process proceeds.
PHASE 2: DOCUMENTATION DEVELOPMENT
Step 6
Documentation and development
There are 6 documented procedures required to create ISO 9001 QMS:
- Document control
- Control of records
- Internal Audit
- Non-Conforming Product
- Corrective Action
- Preventive Action
There are always some additional documented procedures which will be needed for your staff
while they are working the company’s various processes.
Step 7
Organizing and Documenting Your Quality System
Quality Manual – is a key document written early in QMS implementation, it should always be up to date to ensure that the correct process interfaces are defined and organizational chart documented.
The Quality Manual should include:
- A statement explaining the scope of the Quality Management System, including exclusions and details for their justification
- A description of the Quality System processes and their interactions
- The company’s quality policy and quality objectives
- An overview of the system level procedures
Procedures describe the activities of individual departments,
how quality is controlled in each department and
the checks that are carried out.
Work Instructions are specific and contain the necessary instructions
needed to perform a task.
Records must be maintained to show compliance
to quality system requirements.
Records must be kept up to date to prove compliance
during registration or subsequent surveillance audits.
Processes used in the quality framework should be mapped and
updated to meet requirements of the ISO 9001 standard.
Templates should be developed for all of the controlled document types
you intend to use. Templates should have consistent styles and formats
so that documents are easy to read and navigate.
Each template must meet controlled document requirements.
Procedures and Work Instructions should have Purpose, Scope and
Responsibilities sections. A company logo can also be included
with the document header
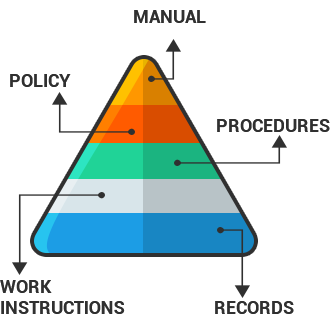
Quality Policy contains Quality Objectives of the organization
which are present at all level and which establish measurable processes
to assure your product or service meets stated requirements.
Documentation Control System must be created to manage the creation,
approval, distribution, revision, storage, and disposal of the various types of documentation
that your company develops. Your document control systems
should be as simple and as easy to operate as possible
but sufficient to meet ISO 9001 requirements
(it should contain a unique ID, revision control, change history summary,
signatures & verification signature, date of versions and revisions).
The principle of ISO 9001 document control
is that employees should have access to the documentation
and records needed to fulfill their responsibilities.
PHASE 3: IMPLEMENTATION
Step 8
Put Quality Management System in practice
Implement quality management system in your company
and conduct training for employees.
Keep records of training,
because in the eye of ISO and FDA without written evidence
training is as good as it never happened.
Step 9
Notified Body selection
Select an independent Registration Body
that is officially accredited to issue Quality System certifications.
They make audit the company’s Quality System
and if it’s successful, it gets certificated.
Step 10
Internal quality audit
As the system is being installed, its effectiveness should be checked
by regular internal quality audits. Internal quality audits are conducted
to verify that the installed quality management system:
- Conform to the planned arrangements, to the requirements of the standard (ISO 9001:2015)
and to the quality management system requirements established by your organization. - Effectively implemented and maintained.
Even after the system stabilizes and starts functioning,
internal audits should be planned and performed as part of an ongoing strategy.
Step 11
Management review

After 3 to 6 months of Quality System operating,
an internal audit and management review should be conducted
in purpose to assure suitability, adequacy and effectiveness of the QMS
and corrective measures implemented.
These review and corrective measures should help improve Quality System
(quality policy and quality objectives included).
The input to management review should include information on:
- Results of audits,
- Customer feedback,
- Process performance and product conformity,
- Status of preventive and corrective actions,
- Follow-up actions from previous management reviews,
- Changes that could affect the quality management system, and
- Recommendations for improvements.
Even after the system stabilizes and starts functioning, internal audits should be planned and performed as part of an ongoing strategy.
Step 12
Pre-assessment audit
A pre-assessment audit should be done by the registration body you selected, after your Quality System has been in operation for a few months.
This audit should be done in 2 stages:
Includes the audit of documentation and making a management review
(Step 11.)
Ensures that all applicable ISO 9001 or related standard requirements have been met and all non-conformances found in stage 1 have been corrected.
Even after the system stabilizes and starts functioning, internal audits should be planned and performed as part of an ongoing strategy.
Step 13
Certification and registration
If the certification body finds the system
to be working satisfactorily, it awards the organization a certificate,
generally for a period of three years.
During this three-year period,
it will carry out periodic surveillance audits
to ensure that the system is continuing to operate satisfactorily.
Step 14
Continual Improvement
Certification shouldn’t be the end. The effectiveness and suitability of the quality management system should be continually improved through the use of
- Quality policy
- Quality objectives
- Audit results
- Analysis of data
- Corrective and preventive actions
- Management review
If you’re ready to get serious about your quality management and product development efforts, qmsWrapper is your solution.